Power Supply Unit (PSU) Circuit Safety Protection SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions & Products
Overview
A PSU (Power Supply Unit) is a core component that provides stable power to servers, storage devices, and networking equipment within a data center. It converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) to ensure the proper operation of the equipment. Key features of a PSU include: high efficiency (often compliant with 80 PLUS certifications like Titanium or Platinum, with over 90% efficiency), redundant design (using N+1 or 2N configurations to ensure continuous power in case of a failure), a modular structure (for easy maintenance and upgrades), intelligent management functions (supporting remote monitoring and load optimization), and high reliability, high-temperature resistance, and low noise. These characteristics are essential for meeting the 24/7 operational and energy-saving needs of a data center.


Why Data Center Power Supply Units (PSUs) Need Circuit Safety Protection
A Power Supply Unit (PSU) in a data center requires circuit safety protection for several key reasons:
Preventing Equipment Damage:
Power fluctuations, overloads, or short circuits can damage critical hardware such as servers and storage devices. Circuit protection (e.g., overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection) effectively prevents these issues and extends equipment lifespan.
Avoiding Data Loss:
Power interruptions or voltage anomalies can lead to data center downtime, causing data loss or corruption. Protection circuits (e.g., UPS systems and surge protectors) ensure power continuity and protect data integrity.
Reducing Fire Risk:
Overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, or equipment overheating can cause fires. Circuit protection devices (e.g., circuit breakers and fuses) can promptly cut off faulty circuits, reducing fire hazards.
Ensuring Personnel Safety:
Data centers involve high-voltage equipment. Circuit protection (e.g., grounding protection and leakage protection) prevents electric shock accidents and ensures the safety of maintenance personnel.
Ensuring Business Continuity:
A data center is a critical business infrastructure. Any power failure can lead to costly downtime. Protection circuits (e.g., redundant power supplies and fast-switching systems) minimize downtime.
Coping with External Interference:
External factors such as lightning strikes and grid fluctuations can cause surges that damage equipment. Surge protectors can absorb overvoltage, protecting the PSU and associated equipment.
Compliance with Regulations and Industry Standards:
Circuit protection is a mandatory requirement of many international and regional safety standards. Data centers must comply with these to ensure legality and avoid legal penalties.
Mandatory Standards and Requirements (For reference only; please refer to actual standards)
IEC 62368-1 (Safety Standard for Audio/Video, Information Technology Equipment):
Requirements:
This standard, which replaced IEC 60950, mandates that PSUs must have protective measures to prevent electric shock, fire, and injury. This includes double insulation, grounding protection, and current-limiting circuit design.
NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code, NEC):
Requirements: Requires each branch circuit to be equipped with an inverse-time or instantaneous circuit breaker that complies with UL 489, or to use CC, J, or R-class fuses for branch circuit protection.
OSHA Electrical Safety Guidelines:
Requirements: Stipulates that high-voltage equipment must be equipped with appropriate grounding, insulation, and overcurrent protection devices, and that access by unauthorized personnel to high-voltage areas must be restricted.
ASHRAE TC 9.9 (Data Center Thermal Management Standard):
Requirements: Requires PSUs and related electrical systems to work in conjunction with efficient cooling systems to prevent circuit failures caused by overheating.
TIA-942 (Data Center Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard):
Requirements: Specifies that data centers must adopt redundant power supply designs and reliable circuit protection measures to ensure high availability and safety.
The circuit safety protection of a data center PSU is a critical measure for ensuring equipment safety, data integrity, and business continuity. It covers functions such as overcurrent, overvoltage, surge protection, and grounding. Mandatory standards such as UL 60950-1, IEC 62368-1, and NFPA 70 require PSUs to have reliable protection mechanisms to prevent electrical faults, fires, and personnel injury, while also meeting compliance needs. These standards collectively ensure that data centers operate safely and stably in high-load and complex environments.
Common PSU Circuit Safety Protection Methods (For reference only)
These protection methods are typically integrated into the PSU design and comply with standards like UL 60950-1 and IEC 62368-1, ensuring the high reliability, safety, and stability of data center power systems.
Overcurrent Protection:
Limits current using a Fuse or Circuit Breaker to prevent damage from overloads or short circuits.
Application:
Automatically cuts off circuits that exceed the rated current, protecting the PSU and downstream equipment.
Overvoltage Protection (OVP):
Detects and limits input or output voltage that exceeds a safe range, preventing high voltage from damaging hardware.
Application:
Absorbs or disconnects abnormally high voltage, such as grid surges or lightning strikes.
Undervoltage Protection (UVP):
When voltage drops below a safe threshold, it automatically disconnects the circuit or switches to a backup power source, preventing equipment failure due to insufficient voltage.
Application:
Copes with sudden drops in grid voltage or unstable conditions.
Short-Circuit Protection:
Quickly cuts off power upon detecting a short circuit, preventing overheating or fire.
Application:
Uses fast-response circuits to protect the PSU and connected equipment.
Surge Protection:
Uses a Surge Protective Device (SPD) to absorb or divert transient surges from lightning strikes or the grid, protecting the PSU from high-voltage shocks.
Application:
Commonly found at the external power input of data centers.
Overtemperature Protection (OTP):
Monitors the internal temperature of the PSU using temperature sensors. When the temperature exceeds a threshold, it reduces power output or shuts down the device to prevent damage from overheating.
Application:
Adapts to the high-temperature operating environment of data centers.
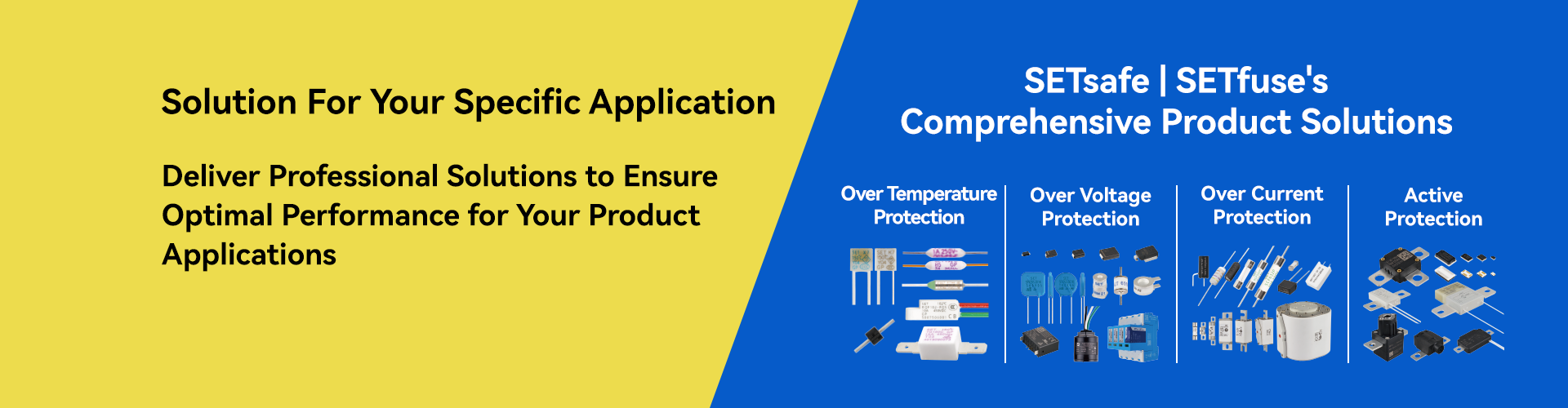
SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions, Protection Types, Products, and Series
For detailed product specifications, please click "Learn more" to view the product detail page.
Protection Type: PSU Overcurrent Protection
Product: Cartrige Fuse-links(CFL)
Series:
SCF632 Learn more
SCF520 Learn more
Protection Type: PSU Overvoltage Protection
Product: Transient Voltage Suppression Diodes (TVS)
Series:
SPC1~4 Learn more
SPCL1~4 Learn more
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production

















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain